Inflation has been on a steady decrease for seven consecutive months from April to November, 2021, indicating an improvement in the economic indices of the nation.
At the last measurement in November, it was put at 15.40 per cent after the nation’s gradual recovery from recession in the fourth quarter of 2020, with a Grvoss Domestic Product (GDP) growth rate of 0.11 per cent from the 6.11 per cent contraction in the third quarter, signaling a gradual recovery from recession.
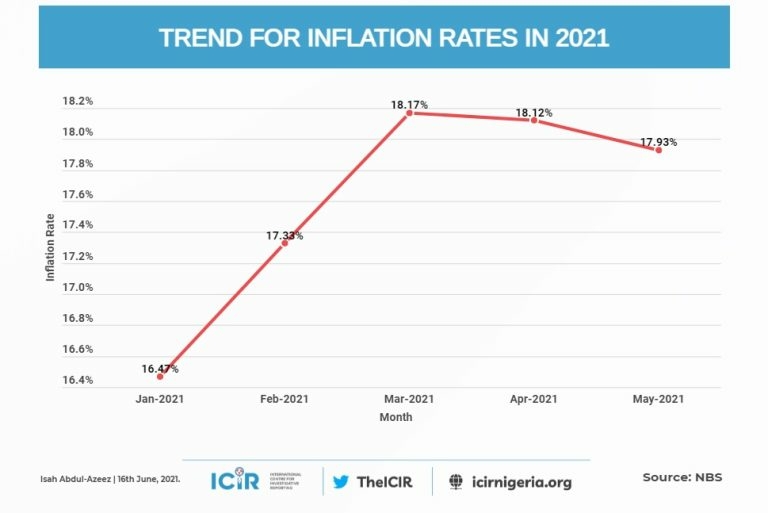
Although this was a positive trajectory, it did not reflect on the inflation rate until April when there was a decline of 0.05 per cent to 18.12 per cent from 18.17 per cent recorded in March.
This decrease continued in May to 17.93 per cent, June recorded 17.75 per cent, July 17.38 per cent, August 17.01 per cent, September 16.63 per cent and October 15.99 per cent.
With this decrease in headline inflation, it is expected that the prices of goods and services are to also reduce.
This is however not so as experts give different reasons for this scenario.
Inflation as defined by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN), depicts an economic situation where there is a general rise in the prices of goods and services, continuously.
“It could be defined as ‘a continuing rise in prices as measured by an index such as the consumer price index (CPI) or by the implicit price deflator for Gross National Product (GNP)’.
“Inflation is frequently described as a state where “too much money is chasing too few goods”. When there is inflation, the currency loses purchasing power.”
“The purchasing power of a given amount of Naira will be smaller over time when there is inflation in the economy.”
“For instance, assuming that N10.00 can purchase 10 shirts in the current period, if the price of shirts double in the next period, the same N10.00 can only afford 5 shirts.”
Ceyda Oner, a deputy division chief in the International Monetary Fund (IMF’s) Finance Department, in an IMF publication titled “Inflation: Prices on the Rise”, said that in measuring inflation, consumers’ cost of living usually depends on the prices of many goods and services and the share of each in the household budget.
“To measure the average consumer’s cost of living, government agencies conduct household surveys to identify a basket of commonly purchased items and track over time the cost of purchasing this basket.”
The National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) says that the construction of the CPI combines economic theory, sampling and other statistical techniques using data from other surveys to produce a weighted measure of average price changes in the Nigerian economy.
It also said that every month, 10,534 informants spread across the country provide price data for the computation of the CPI. The market items currently comprise of 740 goods and services regularly priced.
“The first stage in the calculation of the CPI is the collection of prices on each item (740 goods and services) from outlets in each sector (rural or urban) for each state.”
“Prices are then averaged for each item per sector across the state. The next step is to use the average price to calculate the basic index for each commodity and the current year price of each commodity is compared with a base year’s price to obtain a relative price.”
As to why the decrease in inflation rate may not translate to a decrease in the prices of goods and services, Mr Boniface Amobi, former Director, Macroeconomic Department of the NBS, said it all depends on the factors informing the declining inflation and the prices of goods and services.
According to him, if what is declining the inflation is the prices of food, because it is harvest time and foods are being harvested, it can induce reduction or decline in inflation figures because the prices will go down in terms of food items.
He, however, said that food inflation was very volatile because when there was injection of more food in the country, prices of food items would come down and if anything else happened, like a government policy change or some human factors also changes, it may change in a very short time.
“If for example there is a decline in inflation due to the harvest season and within the same period there is another arm of the government coming up with some policies that are putting fear into the people that maybe there will be removal of fuel subsidy.”
“Also at the same time there will be increase in tariff of electricity or some other thing, it might make the effect of the decline not to be felt because other human factors will nullify it.”
“There will be people who will want to purchase and hoard the goods and once there is pressure on one product it will affect others.”
Amobi also said that in Nigeria, there was the belief that once prices of items go up it could never come down, so everyone would want to increase prices and it becomes an issue.
“So yes, if the thing is going down there are always some human factors in Nigeria that will not allow it to be felt.”
“The people who are measuring the inflation do so with the figures they have because they are not in control of the other factors and they are saying what the data is giving them.”
“So, it is very possible because of the peculiar nature of the Nigerian situation.”
He, however, said that the way forward was to educate the public to know that if the measurement gives a certain figure you could not blame the people measuring it and say they are wrong.
“So, it is really about public awareness and education on what is going on. People should be carried along and there should be advocacy so people can be educated on the findings and the implications.”
The Statistician-General of the Federation, Simon Harry, in his submission, said that demand and pricing according to different markets also affect prices giving the impression that the cost of items were not reducing.
“So, yes, you might say that the price of things in Wuse market is going up, but going back to my village it is not so, rather it is coming down because there are so many factors that are influencing the price.”
“So, the demand factor is there influencing the price of the product and again also in computing the inflation rate the base effect is also influencing it.”
“The base effect has a tendency of making it high or making it come down coupled with some other variables that are driving the process, so it is not enough for you to just take some few markets and then conclude that the prices on the products in these markets are going up.”
He was also of the opinion that even if the prices of some farm produce were not coming down, they were not the same prices as were obtained in February.
“They are not commanding the same prices or higher prices rather, because the months of November and October are harvest periods. So it is either the prices are stable or are coming down gradually.”
“It is a wrong impression to say that prices generally are going up”, he added.
Ona Ohimor, a Financial Consultant, said that a key factor that influences decrease in inflationary pressure was money supply within the economy.
According to him, the scenario of declining inflation amidst rising prices presents a paradox particularly with regards to food prices.
“The reduction in inflation figures month on month appears not to have reflected significantly on food prices and other day to day consumables.”
“The inflation figure (CPI) also known as headline inflation is comprised of sub-indexes. While some sub-indexes might have declined significantly other sub-indexes may experience marginal decrease or increase.”
“Rising food prices may not be unconnected with factors such as insecurity and erosion of the value of the Naira,” he said.
Ohimor added that the government needs to do more to improve on the security situation among other factors impacting on prices of food in general and agricultural produce in particular.
News Agency of Nigeria (NAN)
















Discussion about this post