- The NCDC reports that children aged 0 to 5 are the most affected by Mpox, with 48 confirmed cases this year
- No deaths have been recorded from Mpox in Nigeria this year, despite a rise in suspected cases and confirmed infections
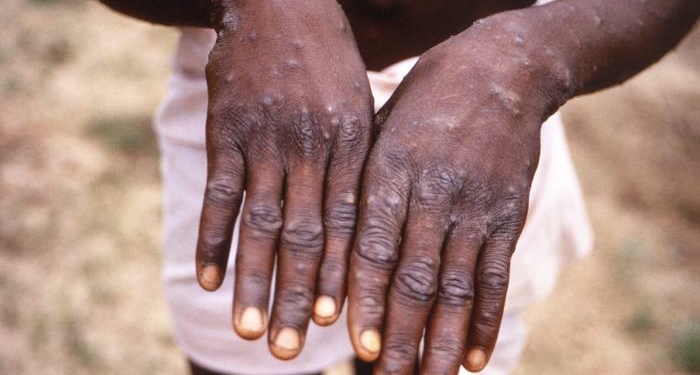
The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) has reported that children between 0 to 5 years old are the most affected age group among the 48 confirmed cases of Mpox recorded this year in Nigeria.
In a situation report for week 34 (August 25) posted on its website on Friday, the NCDC disclosed that 48 confirmed cases of Mpox were recorded out of 868 suspected cases across 35 local government areas in 19 states and the Federal Capital Territory (FCT).
Fortunately, no deaths have been attributed to the disease so far this year. However, 57 new suspected cases were reported in epidemiological (Epi) week 34, 2024, compared to 25 cases reported in the previous week (Epi week 33).
The report states, “Eight confirmed cases were reported in week 34 compared with one (1) confirmed case reported in week 33, 2024. Twenty states and the FCT have recorded at least one confirmed case across thirty-five (35) local government areas in 2024.”
The age distribution of the confirmed cases is as follows:
- Ages 0-10: 17 cases
- Ages 11-20: 7 cases
- Ages 21-30: 9 cases
- Ages 31-40: 8 cases
- Ages 41-50: 7 cases
The cases were recorded in several states:
- Lagos (1), Rivers (2), Bayelsa (6), Abia (1), Delta (2), Imo (1), Edo (1), FCT (2), Anambra (2), Cross River (5), Plateau (2), Akwa Ibom (4), Nasarawa (1), Oyo (1), Kaduna (1), Ebonyi (1), Benue (3), Enugu (8), Osun (2), Kebbi (1), and Zamfara (1).
Mpox is a rare viral zoonotic disease, which means it is transmitted from animals to humans. It occurs sporadically, primarily in remote Central and West Africa villages near tropical rainforests. The disease is caused by the Mpox virus, which belongs to the Orthopoxvirus genus in the family Poxviridae. This genus also includes the variola virus (which causes smallpox), the vaccinia virus (used in the smallpox eradication vaccine), and the cowpox virus (used in earlier smallpox vaccines). Following the eradication of smallpox, the Mpox virus has emerged as the most significant Orthopox virus.
On August 13, 2024, the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention declared Mpox a public health emergency of continental security to address significant public health threats.
The NCDC also stated that the National Mpox multi-sectoral and multi-partner Emergency Operation Centre continues to coordinate the country’s response to the outbreak.







Discussion about this post