You’ve probably used a computer keyboard a million times without even thinking about what each key does. But those little buttons and keys make it possible for us to tell our computers what to do. There’s way more going on under those plastic keys than you might realize.
In this article, we’ll take a tour of the different parts of a computer keyboard so you can finally understand what each part is called and what it does. From the alphanumeric keys you use every day to more obscure keys like Modifier keys, we’ll uncover the purpose behind every single key.
An Overview of the Computer Keyboard
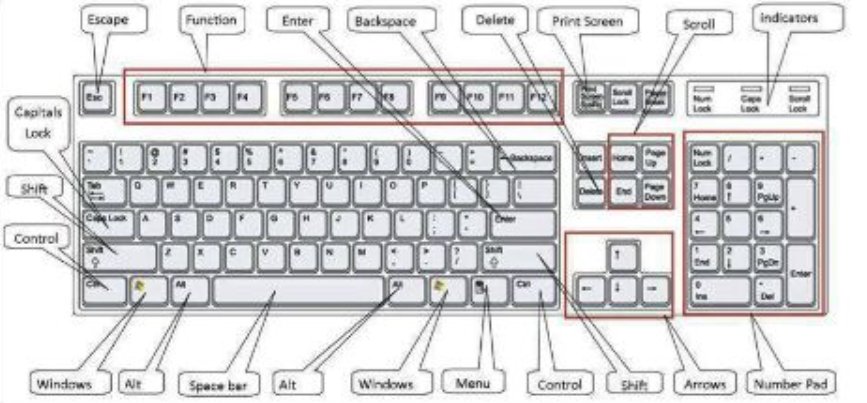
A computer keyboard is an input device that allows users to enter characters and functions into the computer system by pushing buttons or keys. It is the principal device for entering text. A keyboard usually includes keys for individual letters, numbers, and special characters, as well as keys for specialized functions.
The Keyboard Layout
The standard keyboard layout includes alphanumeric keys, punctuation keys, and special function keys. The alphanumeric keys make up the main section and include the letters A through Z, numbers 0 through 9, and symbols like period, comma, and question mark. The function keys, like F1 through F12, perform certain actions like saving files or refreshing web pages.
By understanding the different parts of a standard keyboard, you’ll be typing comfortably and efficiently in no time.
Types of Keyboard
There are several types of keyboards, including standard keyboards, ergonomic keyboards, gaming keyboards, and wireless keyboards.
QWERTY Keyboard
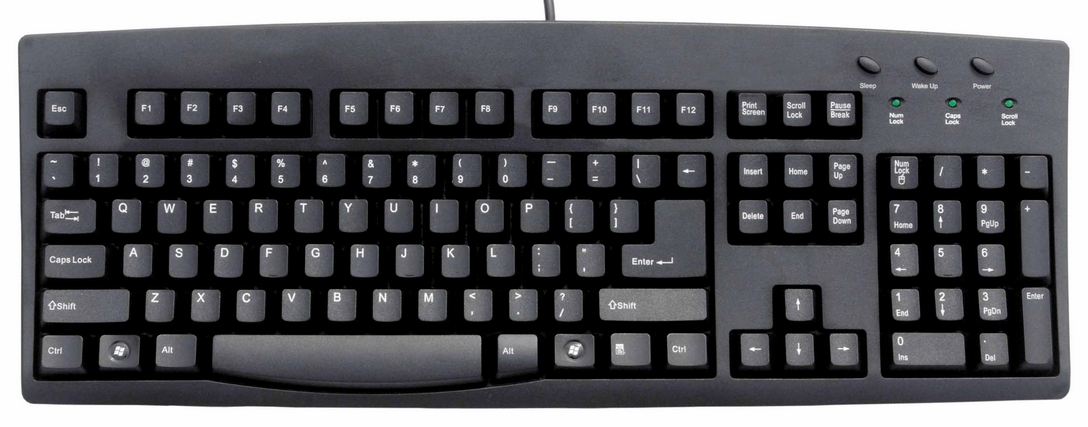

The QWERTY keyboard is the standard and most common type you’ll find. It has the standard QWERTY layout with letters, numbers, and punctuation marks. These are best for basic typing and productivity.
Gaming Keyboard
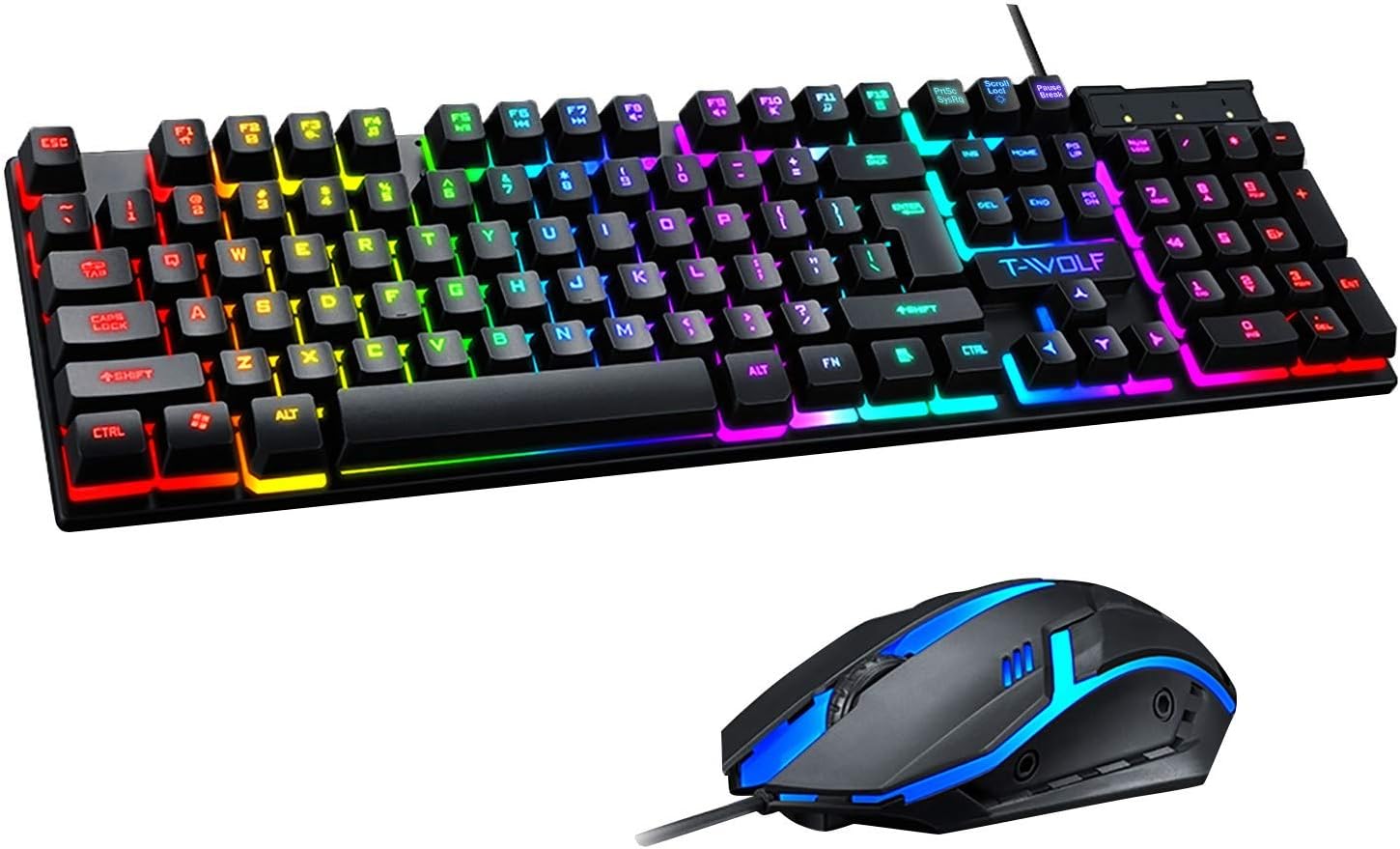

The Gaming keyboards are designed specifically for PC gaming. They often have programmable keys, macro keys, and dedicated media controls. Some gaming keyboards have customizable RGB backlighting and key switches optimized for gaming. These keyboards make it easy to quickly access controls and commands while gaming.
Ergonomic Keyboard
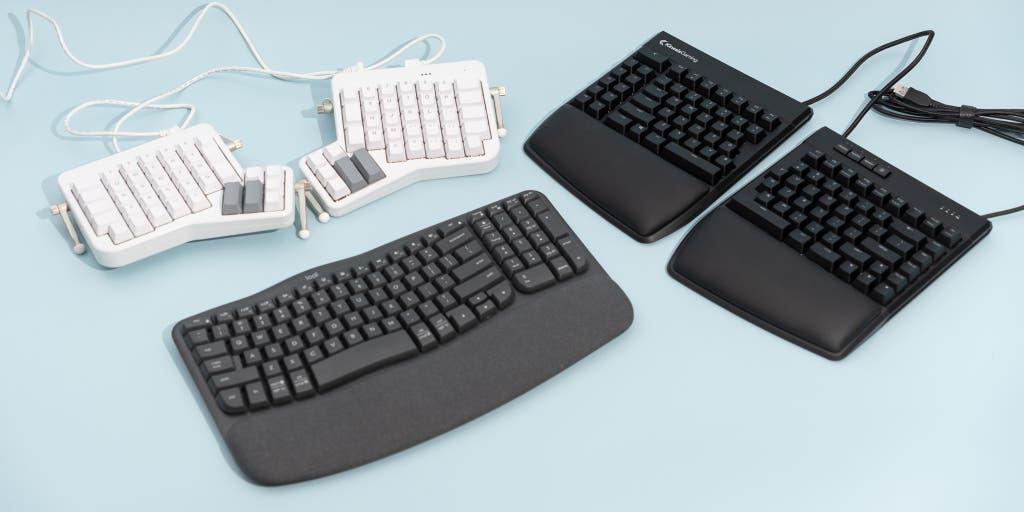

The Ergonomic keyboards are designed to be more comfortable and natural to type on. They often have a curved or split design that positions your wrists and forearms in a neutral alignment. This helps reduce strain and prevents repetitive stress injuries. Ergonomic keyboards can take some getting used to, but they are a good option if you type for long periods.
Compact Keyboard

The Compact keyboards, also known as space-saving keyboards, are smaller in size but retain the standard QWERTY layout. They eliminate extra keys and the number pad to provide a minimalist design. Compact keyboards are good for small desks or when portability is a priority. However, the smaller keys and layout can be difficult for some typists to adjust to.
Wireless Keyboard

A wireless keyboard connects to your computer via Bluetooth or a USB receiver instead of a cable. Wireless keyboards provide more flexibility in how and where you use your keyboard. However, wireless keyboards require batteries, and there can be occasional connectivity issues. For most people, the convenience of wireless outweighs these minor downsides.
So, in summary, there are many types of computer keyboards that suit different needs. The options range from basic to advanced, wired and wireless, compact to full-size. Choosing the right keyboard for you comes down to how you use your computer and personal preferences.
The Parts of a Computer Keyboard
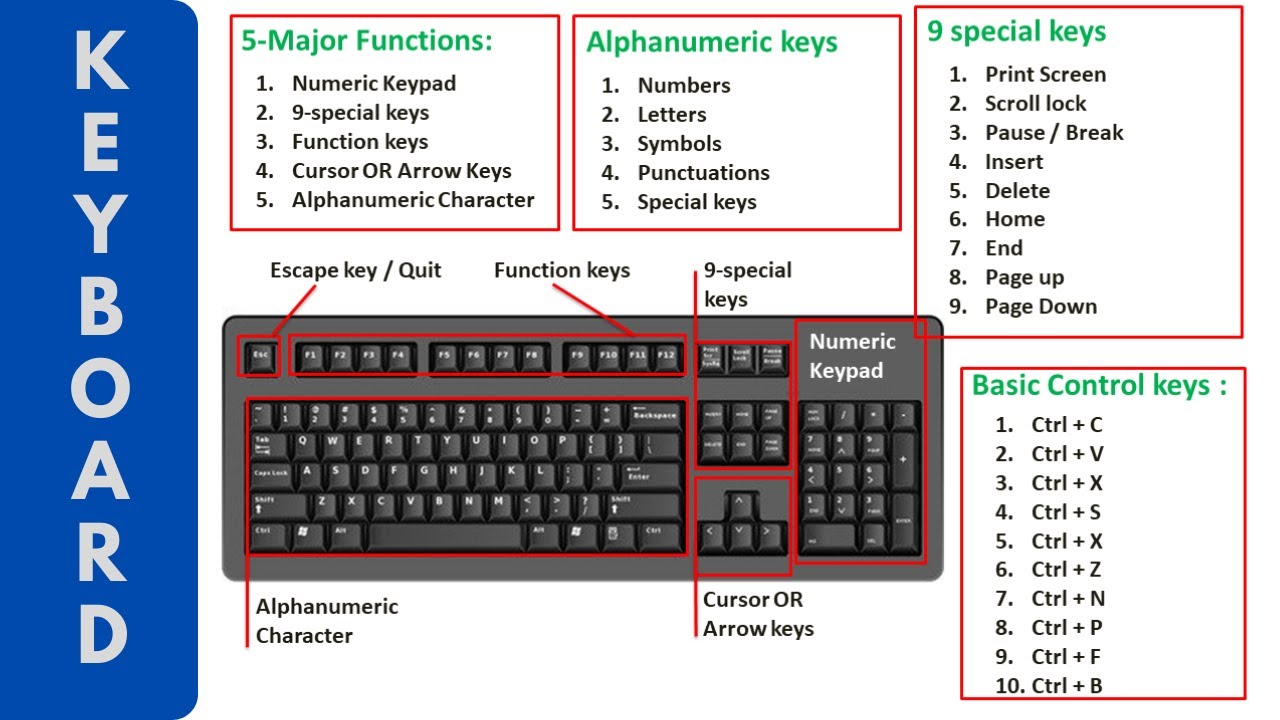
The standard keyboard has several distinct parts, which include the following:
The Alphanumeric Keys The alphanumeric keys on a keyboard allow you to enter letters, numbers, and symbols. Familiarize yourself with the layout of these keys to improve your typing speed and accuracy.
The alphanumeric keys make up the main part of the keyboard.
Letters
The letter keys are arranged in the standard QWERTY layout. Starting at the top left, you have the letters Q, W, E, R, T, and Y. The middle row has A, S, D, F, G, H, J, K, and L. Finally; the bottom row includes Z, X, C, V, B, N, and M. With practice, you’ll get to know this layout by heart.
Numbers
The number keys run along the top of your keyboard. Start with 1 at the far left, going up to 9 on the right. The 0 key is found below the 9. For convenience, the numbers are in ascending order, so you can quickly find the number you need.
Symbols
Various symbols like the question mark (?), exclamation point (!), and ampersand (&) are embedded within the letter keys. Other common symbols, including the asterisk (*), minus sign (-), equals sign (=), and plus sign (+), have their own dedicated keys. Some of the symbol keys include the space bar, enter, and backspace keys.
Memorizing the locations of the alphanumeric keys on your keyboard just takes regular practice. Focus on building muscle memory by typing out the keys in order, starting with the letter rows and then the numbers and symbols. Try typing the keys without looking at the keyboard. Before you know it, alphanumeric entry will become second nature, allowing you to focus on what really matters.
The Numeric Keypad
The numeric keypad, also known as the number pad or numpad, is the section of keys on the right side of the keyboard. These keys allow you to quickly enter numbers and perform basic math functions.
The numeric keypad typically contains the numbers 0 through 9, along with additional keys such as a decimal point, num lock, and math operators like +, -, *, and /. On some keyboards, the num lock key toggles the keypad between entering numbers and acting as directional arrow keys. When the num lock is on, the keys will input numbers. When the num lock is off, some of the keys act as arrow keys to control the cursor.
The number pad is ideal for anyone who frequently needs to enter numbers, such as for accounting, finance, data entry, and more. It allows you to type numbers quickly with one hand without having to reach the number keys at the top of the main keyboard. Many people find a number pad more efficient and ergonomic to use than the number keys for entering numeric data.
Some keyboards also have additional keys on the number pad for calculator functions like equals (=), decimal point (.), and memory keys (M+). The number pad essentially turns your keyboard into a basic calculator, allowing you to perform simple addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division right from your keyboard.
The number pad is a useful feature for many, but not all keyboards have a dedicated number pad. More compact keyboards may omit the number pad to save space. In those cases, you can purchase a separate USB number pad that you plug into your computer if you need one for work or frequent number entry.
In summary, the numeric keypad provides an efficient way to enter numbers and perform quick calculations. For many jobs and tasks, it’s an indispensable part of a keyboard. If your work involves a lot of numbers, you’ll want to make sure any keyboard you buy has a dedicated number pad.
Modifier
The modifier keys are used to modify the input from other keys. Keys like Ctrl, Alt, and Shift are modifier keys. They allow you to produce capital letters and access alternative keyboard functions and keyboard shortcuts. These keys are located at the bottom left and right of the keyboard. Some of the common modifier keys are:
Ctrl Key
The Ctrl key is used in combination with other keys to provide keyboard shortcuts. For example, Ctrl+C is used to copy selected text, Ctrl+V is used to paste, and Ctrl+Z is used to undo an action. These shortcuts can save you a lot of time compared to using a mouse to select options from menus.
Alt
The Alt key is also used in combination with other keys to activate menu options without using a mouse. For example, Alt+F opens the File menu, Alt+E opens the Edit menu. After pressing the Alt key, you can press the underlined letter in a menu option to select that option. The Alt key provides a quick way to access menu options even when your hands are on the keyboard.
Esc
The Esc key is used to cancel or exit from the current task or dialog box. For example, if a dialog box pops up, pressing Esc will close the dialog box. In many applications, Esc can also be used to exit full-screen mode or cancel an editing mode like insert mode. The Esc key provides an easy way to back out of an unwanted operation.
Function Keys F1 to F12
The function keys F1 through F12 are used to perform special functions in some applications and operating systems. The specific functions of these keys vary between applications, operating systems, and keyboard manufacturers. They are labeled as F1, F2, F3, to F12 on the keyboard.
Shift
The shift key is one of the modifier keys found on most computer keyboards that allows you to enter uppercase characters or do other “shifted” functions. When held down while pressing a letter, number, or symbol key, an uppercase version of that character is produced instead. The shift key allows you to access the secondary function of number and letter keys to type symbols. For example, press the shift key plus the 2 key to type an @ symbol.
CTRL Key
The CTRL key is one of the most used keys on a keyboard. Short for “control,” the CTRL key modifies the functions of other keys. When pressed in combination with another key, it performs an alternative action like shortcuts for copy and paste.
Copy and Paste Shortcuts
Two of the most common uses of the CTRL key are copying (CTRL+C) and pasting (CTRL+V). These shortcuts allow you to quickly duplicate text, images, and other content. To copy something, select it and press CTRL+C. Then, place your cursor where you want to paste the item and press CTRL+V. This can save you a lot of time compared to right-clicking and selecting from the menu.
Undo/Redo
Made a mistake? No problem. Press CTRL+Z to undo your last action. Forgot what you undid? Press CTRL+Y to redo it. These useful shortcuts work in many programs and operating systems. Whether you accidentally deleted some text or closed a browser tab you didn’t mean to close, CTRL+Z has got your back.
Selecting and Editing Text
The CTRL key also allows you to quickly select and edit text. To select all content, press CTRL+A. To bold text, select it and press CTRL+B. To italicize text, select it and press CTRL+I. You can also use CTRL+C to copy and CTRL+X to cut selected text. The CTRL key opens up a lot of useful editing possibilities.
Closing Tabs and Windows
If you have multiple tabs or windows open and want to close them quickly, the CTRL key can help. To close a single tab, press CTRL+W. To close a browser window entirely, press CTRL+SHIFT+W. These shortcuts work in most browsers and some other programs as well. No more clicking the little “x” dozens of times to close all your tabs and windows!
The CTRL key is an essential part of efficient computing. Mastering a few of the many CTRL shortcuts will make you faster and more productive.
The ALT Key
The ALT key on your keyboard has several useful functions. ALT stands for “alternate,” and the key is used to activate alternate commands and features. Press and hold the ALT key, then type in a three or four-digit number code on your number pad to trigger a function. These numeric codes were originally intended to allow access to characters not found on a standard keyboard.
One of the most common uses of the ALT key is to open menus in programs and on web browsers. Press and hold ALT, then hit the underlined letter in a menu name to open that menu. For example, in a web browser menu bar, press ALT+F to open the File menu, ALT+E to open Edit, ALT+V for View, and so on. This allows you to navigate menus using the keyboard instead of the mouse.
The ALT key is also useful for keyboard shortcuts. Some common examples are:
- ALT+TAB to switch between open windows
- ALT+F4 to close the active window
- ALT+ENTER to open web links in a new browser tab
- ALT+ESC to cycle through items in the order they were opened
Advanced users often use the ALT key in combination with numeric keypad codes to insert special characters and symbols into documents that are not readily available on the keyboard. For example:
- ALT+0169 to insert the copyright symbol ©
- ALT+0153 to insert the trademark symbol TM
- ALT+0151 to insert the em dash —
If you ever forget a code, you can find full lists of ALT codes and the symbols they produce through an online search. They do vary slightly between fonts and operating systems, so check for the specific codes that match your setup.
The ALT key may seem like a minor part of your keyboard, but taking the time to master its functions can save you a lot of time and frustration. Give the ALT key a try the next time you’re working on your computer, and you may discover some new tricks.
The Escape Key
The Escape key, Esc, is one of the most important keys on your keyboard. Located in the top left corner, the Esc key allows you to exit or cancel the current task.
When you’re typing and make a mistake, hitting the Esc key will clear the error and return the cursor to its previous position. This allows you to retype from that point onward. The Escape key essentially allows you to escape from the current typing sequence.
In many programs and applications, pressing the Esc key will close an open window or dialog box, exiting you from that function. For example, if a popup menu opens that you no longer wish to use, pressing Esc will close that menu. The same is true for error messages or notifications within software. The Escape key is a quick way to cancel those messages.
Gamers frequently use the Esc key to access game menus or close them. While playing, pressing Esc pauses the game and opens an options menu. From there, players can adjust settings, save progress, or quit the game entirely. Once in a menu, pressing Esc again typically closes that menu and returns you to active gameplay.
On some keyboards, especially compact ones, the Esc key may be shortened to just “Esc.” Some full-sized ergonomic keyboards place the Esc key in a slightly different position, but it maintains the same functionality. No matter the keyboard style or layout, the Escape key remains an integral part of using a computer efficiently.
The Function Keys on a Keyboard
The function keys or F keys on your keyboard also serve useful purposes beyond the usual typing letters and numbers. They are the top row of keys on a keyboard that run from F1 through F12. The function keys F1 through F12 are used to perform special functions in some applications and operating systems.
These special keys give you quick access to useful actions like saving files, displaying help menus, and controlling media playback.
About the 12 Function Keys on a Keyboard
The function keys, labeled F1 through F12, are keys on your keyboard that provide shortcuts to functions within the application you’re using. Their specific uses vary between programs, but here’s an overview of their common functions:
- The F1 key is typically used to access Help options in many applications and operating systems. Pressing F1 will often open a Help menu where you can search for assistance on how to do something.
- The F2 key is commonly used to rename selected files or folders. In a document, it may be used to switch between editing and selecting text.
- The F3 key usually activates a search function within an application or file browser. For example, in a web browser, it will focus the cursor in the address bar so you can enter a new web address.
- The F4 key is often used to open a new document or tab or to select an existing tab in applications like word processors, spreadsheets, and web browsers.
- The F5 key typically refreshes or reloads the active window. In a web browser, it will refresh the current web page. In other applications, it may update content or reformat the layout.
- The F6 key switches between applications or browser tabs in some software. It may also move the cursor to different panes or frames within the active window.
- The F7 key usually activates the spelling checker in word-processing applications. It can also toggle special modes in some software, such as full-screen view.
- The F8 key often activates keyboard shortcuts or hotkeys in applications and games. It may also be used to toggle between the normal cursor and a resize cursor in some graphics software.
- The F9 key typically activates menus relating to saving files or settings. For example, it may open a save as dialog box or save all open tabs in a browser.
- The F10 key activates the menu bar in most applications and browsers, allowing you to navigate through options using the arrow keys.
- The F11 key toggles full-screen mode on and off in applications like web browsers, word processors, and media players.
- The F12 key opens the Developer Tools menu in most web browsers. In some applications, like word processors, it may toggle additional toolbars and panes.
The Navigation and Editing keys
All keyboards have dedicated keys for navigating documents and editing text. These allow you to quickly move around, select, cut, copy, and paste text.
Navigation Keys
The arrow keys – ↑ ↓ ← → – are used to move the cursor up, down, left, and right. Holding down the Ctrl key while using the arrow keys will move the cursor word by word instead of character by character. The Page Up and Page Down keys move the cursor up and down by full pages. The Home key moves the cursor to the beginning of the line, while the End key moves it to the end of the line.
Editing Keys
The editing keys allow you to select, cut, copy, paste, and delete text.
- The Shift key is used to select text. Hold down Shift and use the arrow keys to select characters, words, lines, or paragraphs.
- The Ctrl + X shortcut will cut selected text.
- The Ctrl + C shortcut copies selected text.
- The Ctrl + V shortcut pastes cut or copied text.
- The Delete key deletes text to the right of the cursor, while the Backspace key deletes text to the left of the cursor.
- The Ctrl + A shortcut selects all text.
- The Ctrl + Z shortcut undo your last edit, and Ctrl + Y redo an edit.
Using a combination of the navigation and editing keys, you can quickly make changes to documents and move around with ease.
Backspace Key
The backspace key is one of the most frequently used keys on your keyboard. As the name suggests, this key allows you to delete characters that you have just typed. Pressing the backspace key will move your cursor one space to the left and delete whatever character is there.
This key is invaluable when typing, as it allows you to quickly correct mistakes and typos. Rather than retyping an entire word or sentence, you can simply press backspace until you reach your error and make the necessary changes. The backspace key saves you time and frustration, ensuring that your writing is clear and error-free.
Some keyboards also have a “delete” key, which performs a similar function but deletes characters to the right of the cursor instead of the left. The backspace and delete keys are commonly used together when editing text. Pressing backspace will remove a character, and pressing delete will remove the next character to the right. Repeating this process allows you to efficiently remove unwanted text without disturbing the surrounding content.
It’s important to note that pressing the backspace key will not permanently delete the text; it will only remove it from the current document or text field. Anything you backspace can be retrieved by using the “Undo” command, which is common in most text editing software and web applications. The Undo feature allows you to reverse the effects of pressing backspace if you delete something unintentionally.
Some additional points about the backspace key:
- Holding down the backspace key will repeatedly delete text until you release the key. This allows you to quickly erase longer passages of text.
- The backspace key can delete past the visible cursor on screen. Even if your cursor is at the end of a line of text, pressing backspace will continue to delete the preceding characters.
- On some keyboards, the backspace key may be labeled “bs”, “bksp” or have an arrow pointing left. But its function remains the same.
- The size and exact position of the backspace key can vary between keyboards, but it is always located above the Enter/Return key.
The backspace key is a simple but essential part of the computer keyboard. Without it, typing and editing text would be far more tedious and time-consuming. This unassuming key has become crucial for productivity and ease of use.
Media Keys
The media keys on your keyboard allow you to control audio and video playback without having to open any media player. These dedicated keys are designed to work with most major media players like Windows Media Player, iTunes, and VLC Media Player.
The most common media keys are Play/Pause, Stop, Previous Track, Next Track, and Volume Up/Down. The Play/Pause button will start playing the current media (like a song, video, or podcast) or pause it if it’s already playing. The Stop button will stop the playback entirely. The Previous Track and Next Track buttons will go back to the previous media item or skip ahead to the next one, respectively.
The Volume Up and Volume Down keys adjust the volume for all audio playing through your computer. Rather than having to open the volume control panel or media player to adjust the volume, these dedicated keys provide quick access. Some keyboards also have dedicated Mute keys to quickly mute all audio.
Many keyboards now also include additional media keys like:
- Play/Pause: Start or pause playback of media
- Stop: Stop playback of media
- Previous/Next Track: Go to previous or next track
- Volume Up/Down: Increase or decrease volume level
- Mute: Mute or unmute all audio
- Rewind/Fast Forward: Go back or skip ahead in media
- Repeat: Repeat current media item
- Shuffle: Randomize playback order of tracks
The specific media keys on your keyboard will depend on the make and model. Most standard keyboards will have at least the basic Play/Pause, Stop, Previous Track, Next Track, and Volume controls, which work to control most media players on your Windows or Mac computer.
To get the most out of your keyboard’s media keys, you may need to configure the default media player in your operating system’s settings or in the software for your keyboard. The media keys should then work automatically with that default media player.
Window Key
The Windows key is an important key on your keyboard that provides quick access to various Windows features. Located between the Ctrl and Alt keys, the Windows key has the Windows logo on it and is used in keyboard shortcuts to open menus, launch apps, and more.
When you press the Windows key, it will open the Start menu, which contains links to your most used apps, files, and settings. From the Start menu, you can launch apps, search for files or settings, shut down your PC, and access the Control Panel. The Windows key is essential for navigating Windows 10 efficiently.
The Windows key is also used in many keyboard shortcuts to speed up your work. For example, pressing Windows key + E will open File Explorer so you can access your files. Windows key + I will open the Settings app, where you can customize your PC. Windows key + S opens Cortana search, so you can search the web or your PC for anything.
There are many more useful Windows key shortcuts:
- Windows key + D minimizes all windows and shows the desktop
- Windows key + L locks your PC
- Windows key + R opens the Run dialog box to run commands
- Windows key + X opens the Quick Link menu with admin options
- Windows key + Shift + S takes a screenshot and saves it to your clipboard
The Windows key unlocks Windows’ powerful capabilities through the Start menu and keyboard shortcuts. Learning and using these Windows key shortcuts will make you a power user and allow you to be far more productive on your PC. The next time you sit down at your keyboard, try pressing the Windows key and explore all it can do for you.
Shortcut Keys From A to Z
When it comes to keyboard shortcuts, the possibilities are endless. Here are 26 of the most useful Windows keyboard shortcuts from A to Z to boost your productivity:
A for Alt + Tab
Quickly switch between open windows. Hold Alt and press Tab repeatedly to cycle through windows.
B for Backspace
Delete the character before the cursor.
C for Ctrl + C (Copy)
Copy selected text or objects. Use Ctrl + V to paste.
D for Delete
Delete selected text or the character at the cursor.
E for End
Move cursor to the end of the current line.
F for Find
Launch the Find dialog box to search for text. Press Ctrl + F to open.
G for Ctrl + G (Go To)
Open the Go To dialog box and jump to a specific line number.
H for Home
Move the cursor to the beginning of the current line.
I for Insert
Toggle between insert and overtype mode. Overtype mode overwrites text, and insert mode inserts text.
J for Justify
Apply full justification to selected text.
K for Ctrl + K
Insert a hyperlink when editing text.
L for Ctrl + L (Align Left)
Align selected text left. Use Ctrl + R for right align and Ctrl + E for center.
M for Maximize
Maximize the active window to fill the entire screen.
N for New
Open a new blank document, window, or folder.
O for Open
Open a file, folder, or program.
P for Print
Send the active document to the printer.
Q for Ctrl + Q (Quit)
Close the active window or program.
R for Ctrl + R (Refresh)
Refresh or reload the active window.
S for Save
Save the active document. Press Ctrl + S to save.
T for Ctrl + T (New Tab)
Open a new tab in the active window.
U for Undo
Reverse the last action. Press Ctrl + Z to undo.
V for Paste
Paste copied or cut text and objects. Use Ctrl + V to paste.
W for Ctrl + W (Close Tab)
Close the active browser tab or document.
X for Cut
Remove selected text or objects and store on the clipboard. Use Ctrl + X to cut.
Y for Redo
Reverse the last undo action. Press Ctrl + Y to redo.
Z for Ctrl + Z (Undo)
Reverse the last action or command. Press Ctrl + Z to undo.
Uses of Keyboard
These are some of the various uses and functions of a keyboard include:
Typing
The keyboard allows you to type letters, numbers, and symbols onto the computer screen. Whether you’re writing an email, updating a spreadsheet, or coding a program, typing on the keyboard is essential. The standard QWERTY keyboard layout is designed for efficient and comfortable typing.
Shortcuts
Keyboard shortcuts, like Ctrl+C to copy and Ctrl+V to paste, allow you to quickly execute commands without using the mouse. Many applications like word processors, web browsers, and operating systems have keyboard shortcuts to help improve your productivity. Learn the most common shortcuts for the tools you use every day.
Gaming
For PC gaming, the keyboard and mouse are the primary input devices. Gamers can map keyboard keys to control movement, jump, crouch, reload, and activate special abilities. Gaming keyboards often have programmable keys, anti-ghosting features, and ergonomic designs for long play sessions.
Accessibility
For those with limited mobility or visual impairments, the keyboard provides an essential way to interface with a computer. Keyboards can be used with screen reading software, Braille displays, and on-screen keyboards that have high contrast and large text. Specialized keyboards are also available with built-in features to aid accessibility.
Navigation
You can navigate through documents, web pages, file folders, and more using just the keyboard. The arrow, page up/down, home, and end keys are all you need to scroll through content without touching the mouse. The tab key allows you to jump between interactive elements like links, buttons, and form fields.
Conclusion
A standard keyboard gives you everything you need to efficiently input data into a computer. With some practice, these keys will become second nature and allow you to improve your productivity. Take some time to familiarize yourself with the different parts of the computer keyboard so you can get the most out of this important tool.








Discussion about this post